The Hidden Effects of Stress on Mental and Physical Health
How Stress Affects Mental Health

Understanding the Psychological Impact of Stress
Stress can considerably alter one’s mental state and emotional well-being. When exposed to stress over an extended period, individuals may experience heightened anxiety and depressive symptoms. This prolonged exposure can lead to more severe mental health conditions if not addressed promptly. The psychological effects can range from mild irritability to debilitating anxiety disorders.
Additionally, chronic stress often disrupts cognitive functions, affecting memory and decision-making skills. The mind, overwhelmed by stressors, struggles to focus, leading to decreased productivity and increased frustration. It is crucial to recognize these signs early to implement stress management strategies.
Emotional fatigue is another consequence of stress, leading to feelings of helplessness or hopelessness. Such emotional responses can create a vicious cycle, as stress can trigger poor coping mechanisms like substance abuse. Addressing the psychological impact of stress is essential for promoting resilience and overall mental wellness.
Social connections can also suffer under stress, as individuals might withdraw from their support systems. This isolation can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and contribute to a decline in mental health. Encouraging open conversations about stress can foster understanding and support within relationships.
Effective stress management, including therapy, mindfulness, and physical activity, is vital in minimizing the psychological toll of stress. By prioritizing mental health, individuals can break free from the cycle of stress and emotional decline, paving the way for a healthier mindset.
The Connection Between Stress and Physical Health
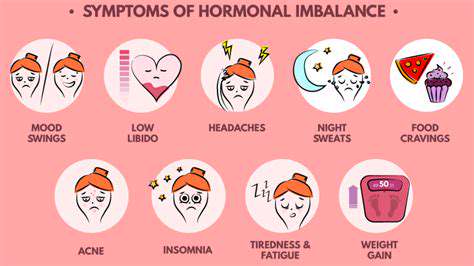
Stress does not only affect mental well-being; it also has profound implications for physical health. Chronic stress can lead to a range of physiological reactions, increasing vulnerability to various health issues. The body's stress response may manifest in physical ailments, such as headaches, muscle tension, and gastrointestinal problems.
Moreover, prolonged exposure to stress elevates cortisol levels, which can contribute to serious health conditions, including hypertension and heart disease. This correlation emphasizes the need for effective stress management techniques to mitigate its physical effects. Poor lifestyle choices linked with stress, such as unhealthy eating or lack of exercise, further exacerbate these physical health risks.
Immune function can weaken under chronic stress, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Regularly high levels of stress can compromise the body's ability to heal and recover from injuries, illustrating the intricate link between mental and physical health. Recognizing and addressing stress can foster a more robust immune system and better overall health.
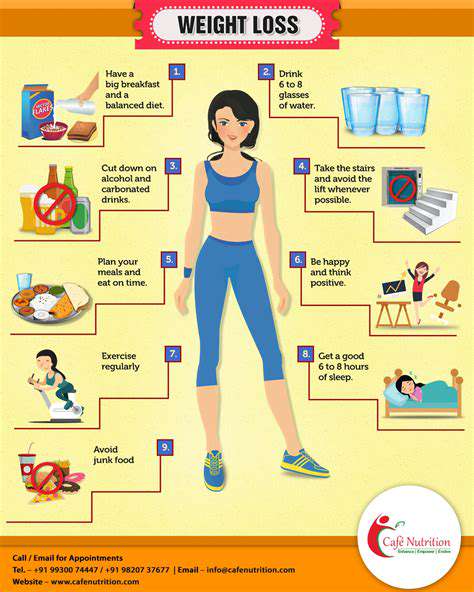
It's essential to engage in healthy practices to combat the physical manifestations of stress. Regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, and balanced nutrition can mitigate these effects and improve both mental and physical health. Incorporating stress-relief techniques, like yoga or meditation, can also be beneficial.
In summary, understanding the interconnectedness of stress, mental, and physical health is crucial. By acknowledging and addressing the hidden effects of stress, individuals can take proactive steps toward a healthier, more balanced life.
The Physical Impact of Stress

The Body's Response to Stress
When an individual experiences stress, the body reacts with the fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormonal changes prepare the body to respond to perceived threats, making it crucial for survival in short bursts. However, when stress becomes chronic, it can lead to numerous health complications.
Prolonged stress can result in physical ailments, ranging from headaches and stomach issues to more severe conditions such as cardiovascular diseases. It's essential to recognize the signs of stress before they escalate into more serious health problems. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate these effects.
Moreover, stress can influence the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses. A weakened immune response can lead to frequent colds and other infections, showing how intertwined mental and physical health really are.
Stress and the Cardiovascular System
One of the most significant impacts of stress is on the cardiovascular system. Chronic stress can lead to increased heart rate and higher blood pressure, known risk factors for heart disease. Managing stress effectively is vital for heart health.
Additionally, stress can cause inflammation in the arteries, further complicating cardiovascular health. This inflammation can lead to the development of plaque, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Understanding the relationship between stress and heart health is crucial for prevention.
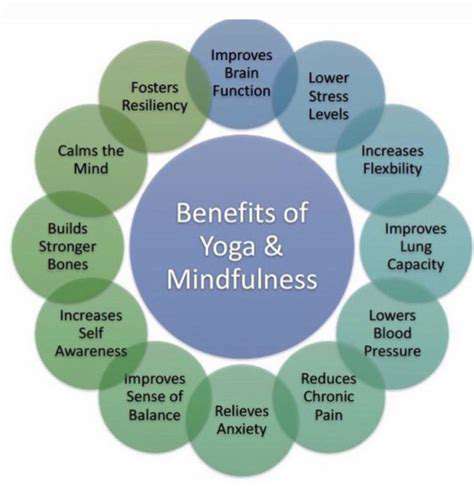
Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as regular exercise, deep breathing, and mindfulness can significantly improve cardiovascular health. These practices can help lower blood pressure and promote a healthier heart.
The Connection Between Stress and Mental Health
Stress is not just a physical experience; it can greatly affect mental well-being as well. Chronic stress is closely linked to mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Recognizing the signs of mental stress is the first step toward seeking help.
When stress becomes overwhelming, it can impair one's ability to think clearly and make decisions, leading to further complications in both personal and professional life. Those affected may find themselves in a negative cycle, where stress exacerbates mental fatigue and vice versa.
Taking proactive steps to manage stress, such as therapy and social support, can help break this cycle. Developing coping strategies allows individuals to handle life's challenges more effectively, improving overall mental health.
Impact of Stress on Sleep Quality
Stress can significantly disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or poor-quality sleep. A lack of restorative sleep can negatively affect both mental and physical health, creating a vicious cycle. Quality sleep is essential for recovery and overall well-being.
Individuals under stress may find it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep due to racing thoughts and heightened anxiety. This lack of sleep can, in turn, heighten stress levels, making it essential to address the root causes of stress for better sleep outcomes.
Implementing relaxation techniques before bedtime, such as reading or meditation, can help promote better sleep. By prioritizing sleep hygiene, individuals can improve their resilience to stress and enhance their overall health.
The Long-term Consequences of Chronic Stress
Over time, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. It can lead to conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Recognizing the long-term consequences of stress is crucial for individual health management.
Many people may experience an increase in unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating, substance abuse, or social withdrawal, further exacerbating health issues. These behaviors can create a downward spiral, impacting relationships and overall quality of life.
Addressing chronic stress through lifestyle changes, mindfulness, and professional support can mitigate these long-term health risks. Making stress management a priority is essential for achieving a balanced and healthy life.
Coping Strategies for Stress Management
Mindfulness and Meditation Techniques
Mindfulness is the practice of staying present in the moment, which can significantly reduce stress levels. By focusing on your immediate surroundings and sensations, you can help calm the mind and decrease anxiety. Techniques such as deep breathing can anchor your awareness and create a sense of tranquility.
Meditation, particularly guided meditation, can also be a powerful tool to manage stress. Spending just a few minutes a day in a quiet place, focusing on your breath, or listening to a guided session can create a mental refuge. Over time, this practice can lead to a lasting reduction in stress and improved emotional resilience.
Incorporating mindfulness and meditation into your daily routine does not require significant time commitment. Simple practices like eating mindfully, where you take the time to appreciate the textures and flavors of your food, can contribute to a greater sense of calm and reduce stress.
Physical Activity and Relaxation Techniques
Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to combat stress. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural stress relievers. Activities such as walking, running, or yoga not only improve physical fitness but also enhance mood and promote relaxation.
Additionally, relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing exercises can be beneficial. Practicing these techniques allows you to reduce muscle tension and lower your heart rate, leading to a more relaxed state. Setting aside time for these activities can make a notable difference in how you cope with stress.
Furthermore, incorporating hobbies that promote relaxation, such as gardening, painting, or reading, provides an excellent outlet for stress relief. Engaging in enjoyable activities can serve as a distraction, helping you unwind and recharge your mental batteries.