Essential Components of Emotional Intelligence for Personal and Professional Growth
Self-Awareness: The Foundation of Emotional Intelligence

Understanding Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior. It is the cornerstone of emotional intelligence and plays a crucial role in personal and professional growth.
When individuals are self-aware, they can assess their strengths and weaknesses accurately. This allows for better decision-making and enhances the ability to manage social interactions.
Building Self-Awareness Practices
There are several practices that can help enhance self-awareness, such as journaling, mindfulness meditation, and seeking feedback from others. Regularly reflecting on one’s feelings and reactions can also improve understanding of personal emotional triggers.
Engaging in these activities consistently can lead to profound insights about oneself. Ultimately, increased self-awareness leads to improved emotional regulation and healthier relationships.
The Impact of Self-Awareness in Professional Settings
In a professional context, self-awareness can significantly influence leadership abilities and team dynamics. Leaders who understand their own emotions are better equipped to inspire and motivate their teams effectively.
Moreover, self-aware employees can navigate workplace challenges more adeptly, fostering a more collaborative and positive environment. Recognizing personal emotional responses enables better conflict resolution and enhances overall team performance.
Self-Regulation: Managing Emotions Effectively
Understanding Self-Regulation
Self-regulation is a crucial component of emotional intelligence, encompassing the ability to manage one's emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations. It involves monitoring emotional triggers and maintaining control over impulsive reactions, allowing individuals to respond in a measured and thoughtful manner. By developing self-regulation skills, individuals can enhance their decision-making processes, leading to more constructive outcomes both personally and professionally.
Furthermore, self-regulation contributes to resilience. It helps individuals cope with stress, setbacks, and challenges without succumbing to negativity or frustration. By practicing self-regulation, one can cultivate a positive mindset that not only aids in personal growth but also fosters a harmonious work environment, improving team dynamics and collaboration.
Strategies to Improve Self-Regulation
Improving self-regulation requires conscious effort and the application of specific strategies. One effective technique is mindfulness, which encourages individuals to be present in the moment and observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment. Mindfulness practices such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises can help increase awareness of emotional triggers, allowing for more intentional responses rather than automatic reactions.
Another strategy is goal setting, where individuals can define clear, achievable objectives related to their emotional responses. By setting realistic goals for emotional management, individuals can track their progress and create a framework for improvement. This not only helps in regulating emotions but also enhances motivation and accountability in both personal and professional contexts.
Motivation: The Drive for Success
Understanding Motivation: Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic
Motivation plays a crucial role in driving individuals towards their goals, both personally and professionally. It can be classified into two main types: intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation refers to the internal drive to accomplish tasks for their own sake, such as personal growth, enjoyment, or a sense of achievement. Conversely, extrinsic motivation is influenced by external factors, such as rewards, recognition, or peer pressure.
Recognizing the type of motivation that resonates with an individual can help tailor approaches to goal-setting and personal development strategies. For example, someone motivated intrinsically may thrive in creative environments that allow for self-expression, while those driven extrinsically might excel in structured settings that provide clear rewards for performance.
The Role of Goal Setting in Motivation
Effective goal setting is essential for maintaining motivation. By establishing clear, attainable goals, individuals create a roadmap that guides their actions and decisions. Goals not only provide direction but also help measure progress, which can further enhance motivation. The SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—can be an effective framework for setting goals that foster motivation.
A well-defined goal can boost self-confidence and drive individuals to push beyond their limits. Additionally, revisiting and adjusting goals as circumstances change can keep motivation levels high and prevent burnout, ensuring sustained commitment to personal and professional growth.
Building Resilience Through Motivation
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from setbacks and challenges, and it is deeply linked to motivation. An individual with high motivation is more likely to view obstacles as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable barriers. This mindset encourages perseverance, allowing individuals to tackle difficulties with determination and a positive attitude.
Moreover, cultivating resilience often requires creating a supportive environment and surrounding oneself with positive influences. Engaging with mentors, participating in group activities, and seeking feedback are all strategies that can enhance motivation and contribute to developing a resilient attitude towards life's challenges.
Strategies to Enhance Motivation
There are several effective strategies for enhancing motivation that can be applied in both personal and professional settings. One such strategy is the practice of positive self-talk, which involves fostering an optimistic inner dialogue. By reframing negative thoughts and focusing on strengths, individuals can build confidence and motivation to pursue their goals.
Another strategy includes creating accountability through social support. Sharing goals with friends, family, or colleagues can create a sense of obligation and encouragement that bolsters motivation. Regular check-ins and celebrating small victories together can reinforce commitment and maintain high motivation levels over time.
Empathy: Connecting with Others
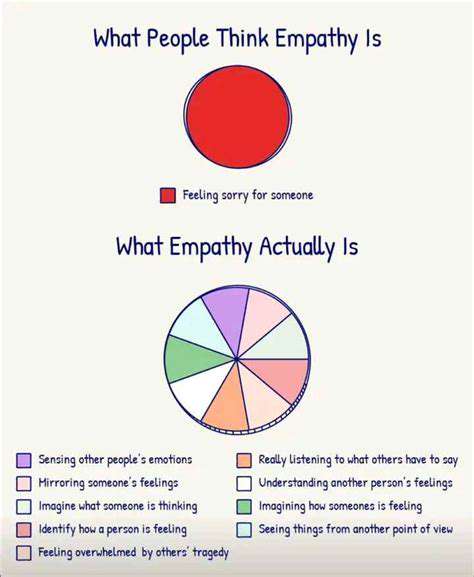
Understanding Empathy
Empathy involves the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. It is a critical component of emotional intelligence that enables us to connect with others on a deeper level. This skill allows individuals to build meaningful relationships, enhancing both personal and professional interactions.
There are two main types of empathy: cognitive empathy and emotional empathy. Cognitive empathy refers to the ability to understand someone else's perspective, while emotional empathy involves sharing the feelings that another person is experiencing. Both forms are essential for effective communication and collaboration.
By cultivating empathy, individuals can create a supportive environment where ideas and emotions are freely exchanged. Such environments often lead to improved teamwork, increased creativity, and greater job satisfaction.
Empathy in the Workplace
In professional settings, empathy plays a crucial role in leadership and team dynamics. Leaders who demonstrate empathic behaviors can foster loyalty and motivation among team members. It also helps to reduce conflict, as understanding each other’s feelings can lead to more effective resolutions.
Workplaces that prioritize empathy are likely to experience higher employee engagement and productivity. When employees feel understood and valued, they are more likely to contribute positively to group dynamics. This ultimately can lead to enhanced overall performance for the organization.
Moreover, empathy in the workplace contributes to a culture of inclusion and respect. When team members practice empathy, it creates a more harmonious work environment that embraces diversity and innovation.
Developing Empathy Skills
Developing empathy requires intentional practice and self-reflection. One effective method is active listening, where individuals focus on truly understanding what others are saying without planning their responses. This approach helps to strengthen the bond between individuals through mutual understanding.
Engaging in conversations with diverse groups of people can also enhance empathetic capabilities. Exposure to different perspectives broadens one’s awareness and understanding of various emotional experiences. It is essential to approach these interactions with an open mind, as this fosters genuine connections.
Additionally, seeking feedback from peers about one's ability to empathize can provide valuable insights. This feedback can guide further development and highlight areas for improvement in interpersonal relationships.
The Impact of Empathy on Mental Well-Being
Empathy not only benefits interpersonal relationships but also enhances individual mental well-being. It allows individuals to feel connected, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation. Furthermore, the act of helping others can lead to increased happiness and fulfillment in one’s own life.
Practicing empathy can also lead to better emotional regulation. When individuals can understand the emotions of others, they become more adept at managing their own feelings and reactions. This skill is vital for maintaining personal and professional relationships.
Moreover, empathy can serve as a protective factor against stress. By forming strong supportive networks, individuals can experience reduced levels of anxiety and depression, leading to a healthier emotional state overall.
Barriers to Empathy
While empathy is a valuable skill, there are barriers that can hinder its development. One significant barrier is stress, which can cloud judgment and reduce one’s capacity for empathy. When overwhelmed, individuals may prioritize their own needs over understanding others, leading to disconnection.
Cultural differences can also pose challenges to empathy. Different backgrounds can influence how emotions are expressed and perceived. It is crucial to recognize and respect these differences to build understanding among diverse populations.
Lastly, emotional fatigue can impede empathetic abilities. When individuals experience compassion fatigue, they may become desensitized, affecting their ability to empathize effectively. It can be beneficial to engage in self-care practices to replenish emotional energy and remain connected to others.
Social Skills: Building and Maintaining Relationships
Importance of Social Skills
Social skills are crucial in both personal and professional settings as they facilitate effective communication and understanding. Establishing clear communication helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters an environment where individuals feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and emotions.
Moreover, having strong social skills enables one to build trust with others. When people feel that they can trust someone, they are more likely to engage openly and work collaboratively, which can lead to more productive relationships.
In the workplace, good social skills can enhance teamwork and collaboration. Team members with strong interpersonal skills are often more adept at resolving conflicts, encouraging cooperation, and motivating one another to achieve common goals.
Techniques for Developing Social Skills
Active listening is a foundational technique for improving social skills. It involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to what others are saying. This skill not only enhances communication but also shows others that their opinions and feelings are valued.
Engaging in empathy exercises can also significantly improve one’s social skills. By putting oneself in another’s shoes, individuals can better understand different perspectives, which is key to building strong relationships.
Practicing open body language and maintaining eye contact are simple yet effective ways to convey attentiveness and openness. This non-verbal communication reinforces verbal messages and strengthens interpersonal connections.
Impact of Social Skills on Professional Growth
In the professional realm, possessing strong social skills can lead to more effective networking opportunities. Networking plays a vital role in career advancement, and individuals with good social acumen are often more successful at building these valuable connections.
Moreover, enhanced social skills can lead to better leadership opportunities. Leaders who demonstrate empathy and excellent communication skills are viewed more favorably and are often more effective at inspiring their teams.
Organizations with members who exhibit strong social skills tend to have higher employee morale and lower turnover rates. Fostering a positive work environment contributes not only to personal satisfaction but also to overall organizational success.
Challenges in Developing Social Skills
Despite the importance of social skills, many individuals face challenges in developing them. Social anxiety can hinder effective communication and may prevent individuals from engaging in social interactions, impacting both personal and professional relationships.
Cultural differences can also pose challenges in social skill development. Understanding and respecting diverse communication styles is essential in today’s globalized workforce, and failing to do so can lead to misunderstandings.
Lastly, a lack of self-awareness can impede the growth of social skills. Individuals must reflect on their own communication habits and areas for improvement to cultivate the necessary skills for engaging with others effectively.