Maximize Your Productivity with the Eisenhower Matrix
What is the Eisenhower Matrix?
Understanding the Quadrants of the Eisenhower Matrix
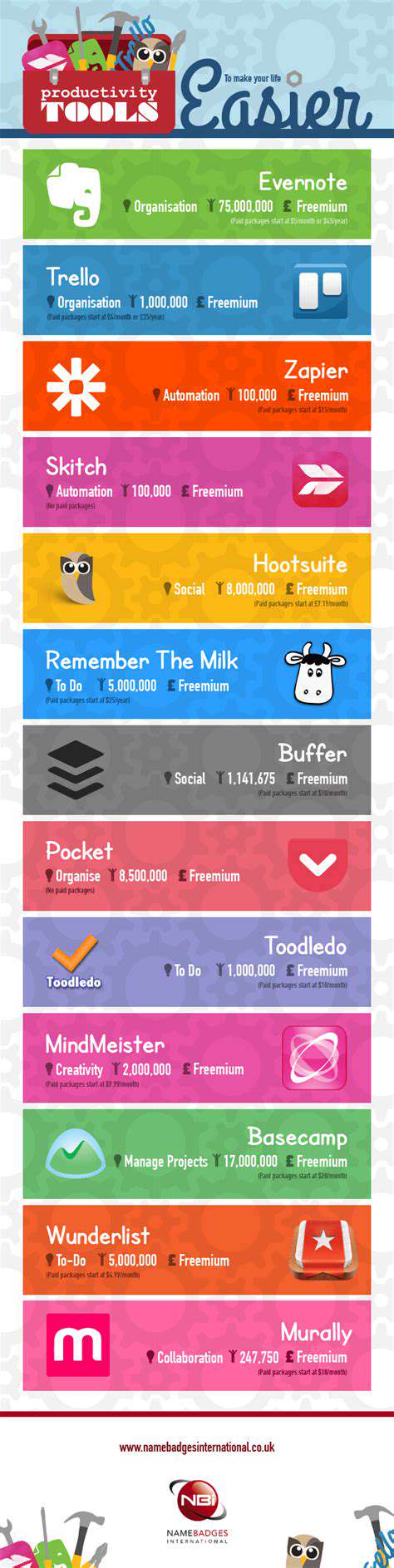
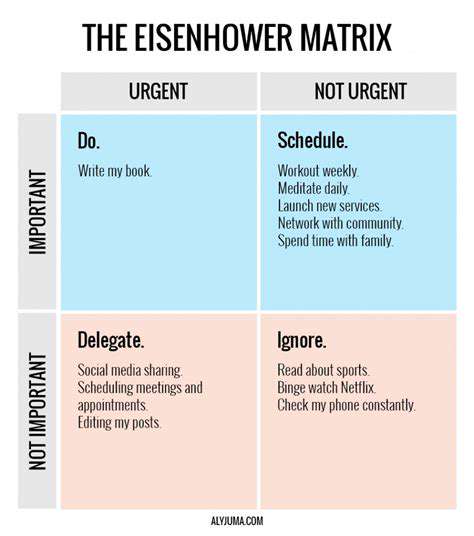
The Eisenhower Matrix is a strategic tool for prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance. It divides tasks into four distinct quadrants: urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, and neither urgent nor important. By categorizing tasks in this manner, individuals can focus on what truly matters, enhancing their overall productivity.
The first quadrant includes tasks that require immediate attention and are critical to success. These tasks usually have deadlines that must be met and can lead to significant consequences if neglected. For example, responding to a critical email from a client may fall into this category.
In the second quadrant lies important tasks that are not necessarily urgent. These tasks contribute to long-term goals and personal growth. For instance, planning for a future project or developing new skills can be aligned with this quadrant. Recognizing and prioritizing these tasks can lead to improved effectiveness and success over time.
The third quadrant contains urgent but unimportant tasks, often filled with distractions. These might include interruptions or tasks that seem pressing but do not contribute significantly to your goals. Learning to delegate or minimize these tasks is essential for maintaining focus on what truly matters.
How to Implement the Eisenhower Matrix Effectively
To effectively implement the Eisenhower Matrix, start by identifying and listing all tasks you need to accomplish. Once you have a comprehensive list, categorize each task into one of the four quadrants. This visual organization helps clarify what you should tackle first and what can be deprioritized.
After categorizing the tasks, focus your immediate efforts on completing those in the first quadrant. Be mindful of the time allocated to tackle these urgent and important tasks, ensuring they are not overlooked. This will provide a sense of accomplishment and maintain momentum.
For tasks in the second quadrant, set aside dedicated time each week to address these important but not urgent activities. This proactive approach ensures that you are continually working on your long-term objectives without getting bogged down by the day-to-day urgency of tasks.
Finally, revisit your matrix regularly. As tasks are completed and new ones arise, your priorities may change. Regularly updating your Eisenhower Matrix will keep you aligned with your goals and ensure that your productivity remains high.
How to Use the Eisenhower Matrix

Understanding the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is a powerful productivity tool that helps individuals prioritize their tasks based on urgency and importance. It divides tasks into four distinct quadrants:
Quadrant I includes urgent and important tasks, which require immediate attention. These tasks are often crises or deadlines that need to be addressed right away.
Quadrant II contains important but not urgent tasks. These are essential for long-term goals and personal development, but they can often be overlooked due to daily pressures.
Quadrant III houses urgent but not important tasks. These tasks may seem pressing but do not significantly contribute to your goals, and brainstorming how to delegate or minimize them can be beneficial.
Lastly, Quadrant IV consists of tasks that are neither urgent nor important. These are distractions that can often clutter your schedule and waste valuable time.
Implementing the Matrix in Daily Life
To effectively implement the Eisenhower Matrix, start by listing all tasks you need to complete. Break them down into the four quadrants based on their urgency and importance.
By visualizing your tasks in this way, you can better manage your workflow. This clarity allows you to understand which tasks are worthy of your time and energy.
Set aside time each week to review and update your matrix. This will help you stay aware of shifting priorities and ensure nothing important slips through the cracks.
Utilize digital tools or apps that allow for easy categorization of tasks. This can streamline the process and make it simpler to adjust as required.
Communicate with team members or peers about the tasks in your matrix to align efforts and expectations. Collaboration can enhance productivity and foster a supportive work environment.
Overcoming Challenges with the Matrix
One common challenge when using the Eisenhower Matrix is identifying which tasks fall into each quadrant. To overcome this, regularly ask yourself questions to clarify the urgency and importance of tasks.
It’s also vital to be honest about your workload and to prioritize effectively. Sometimes, tasks may feel urgent but lack real significance, so take the time to evaluate them realistically.
Another challenge can be the temptation to focus on Quadrant III tasks, which feel urgent but bring little value. Learn to recognize these distractions and set boundaries around them.
Usage of the matrix can be hindered by fluctuating priorities; thus, don’t hesitate to revisit and adjust your quadrants as new tasks arise.
Lastly, practicing self-discipline is essential. Adhering to your matrix can significantly enhance your productivity and help manage time more effectively over the long run.
The Benefits of the Eisenhower Matrix
The Importance of Prioritization
To increase productivity effectively, it is crucial to prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance. The Eisenhower Matrix helps individuals distinguish between what is urgent and what is genuinely important. By categorizing tasks into four quadrants, one can easily visualize where their focus should lie. This approach reduces stress and enhances decision-making, allowing for a more structured day. Ultimately, effective prioritization fosters a clearer path to accomplishing goals.
One significant benefit of this prioritization is that it minimizes distractions. By concentrating on the essential tasks, you can avoid spending time on less critical activities. This focus not only improves work quality but also increases the likelihood of meeting deadlines. Additionally, breaking tasks down into manageable sections can prevent overwhelm and encourage a proactive approach to work.
Moreover, understanding which tasks require immediate attention can lead to better time management. This holistic understanding of your workload enables you to allocate time more efficiently and makes it easier to set boundaries against unnecessary interruptions.
As you refine your prioritization skills, you will likely find that your overall productivity increases. By regularly utilizing the Eisenhower Matrix, you cultivate a habit of continuously assessing your tasks and making informed decisions about where to direct your efforts.
Enhancing Focus and Reducing Stress
Another benefit of utilizing the Eisenhower Matrix is that it enhances focus. When tasks are clearly categorized, it becomes easier to concentrate on what needs to be done without feeling scattered. This clarity can lead to greater efficiency, as fewer mental resources are wasted on indecision and distraction. When you know what tasks are critical, staying on track becomes more achievable.
Additionally, the matrix helps reduce stress. By organizing tasks into a visual framework, it alleviates the burden of uncertainty regarding what to do next. This structured approach minimizes feelings of overwhelm and ensures that you address high-priority tasks first. As a result, people often feel a sense of accomplishment as they complete each quadrant systematically.
Another way the Eisenhower Matrix contributes to stress reduction is by promoting a balance between urgent and important tasks. This balance encourages individuals to incorporate time for planning, reflection, and self-care, which are crucial for long-term success. These components are often neglected in a hurried work environment, but they are necessary for maintaining creativity and motivation.
Finally, regularly using the Eisenhower Matrix fosters a growth mindset. By continuously evaluating tasks and outcomes, individuals can learn from past experiences and adjust their strategies accordingly.